We will perform here a simple evaluation of three common chromatic adaptation algorithms. We find all necessary
tools for this evaluation elsewhere on this site, in the ColorChecker Calculator
and the Chromatic Adaptation Calculator.
Let's look at the ColorChecker "Red" color (third row, third column of the chart) relative to reference illuminants A and C.
The ColorChecker Calculator shows the true values for this color, relative to each illuminant to be:
If we then take the XYZ for illuminant A and adapt it to illuminant C using the Chromatic Adaptation Calculator, we get three
more XYZ values (one for each adaptation method):
Each of these adapted XYZ colors is then compared against the actual illuminant C value from the previous table. For this
comparison, it is useful to first convert all XYZ values to Lab (using the CIE Color Calculator)
and then measure the color difference in ΔE (using the Color Difference Calculator).
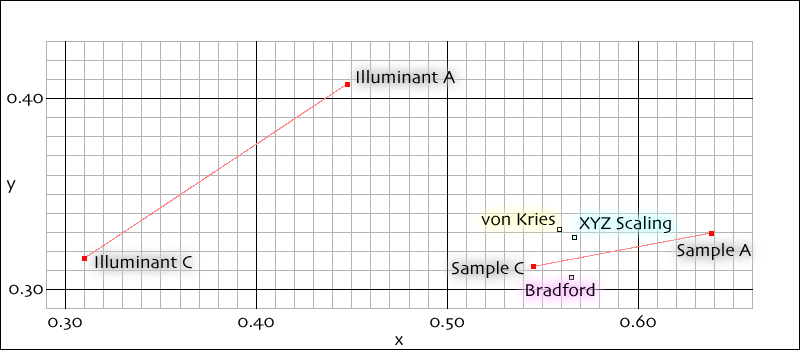
The following illustration shows what happens. The two reference illuminants are shown, connected by a line, as Illuminants
A and C. The actual ColorChecker sample colors are also shown, connected by a line, as Samples A and C. Then Sample A has been
adapted from illuminant A to illuminant C three times, each with a different adaptation method. You can see that none of the adapted
values is exactly the same as the actual Sample C, but they have moved the color in the right general direction.
The above calculation was performed using the first 18 ColorChecker colors (all chromatic adaptation methods yield the same,
perfect results for neutrals, so I chose to exclude the six neutral patches from the evaluation), and all combinations
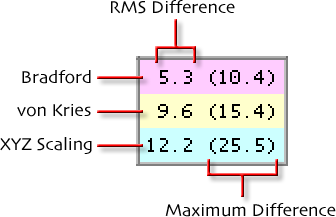
mapping between every possible pairing of the eight reference illuminants. The table below shows the results. The values
in this table represent the following, always expressed in ΔE:
You can see from the table that Bradford is superior to von Kries, which in turn is superior to XYZ Scaling. You can also
see that the adaptation is only an approximation to the true value, and that this approximation is worse when the
two reference illuminants are very different from each other. Adaptation also becomes progressively less perfect as the color
is farther away from neutral.
| From |
To |
| A |
B |
C |
D50 |
D55 |
D65 |
D75 |
E |
| A |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 3.9 ( 7.4) |
| 6.8 (10.1) |
| 7.7 (16.1) |
|
| 5.3 (10.4) |
| 9.6 (15.4) |
| 12.2 (25.5) |
|
| 4.3 ( 8.1) |
| 7.2 (10.6) |
| 7.7 (15.6) |
|
| 4.9 ( 9.4) |
| 8.2 (12.2) |
| 9.1 (18.7) |
|
| 5.7 (11.2) |
| 9.7 (15.2) |
| 11.4 (23.7) |
|
| 6.2 (12.4) |
| 10.8 (17.5) |
| 13.2 (27.4) |
|
| 4.4 ( 7.8) |
| 7.9 (13.6) |
| 9.8 (20.5) |
|
| B |
| 3.9 ( 7.1) |
| 6.5 ( 9.4) |
| 7.7 (16.1) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.8 ( 4.5) |
| 4.7 ( 9.4) |
|
| 0.6 ( 1.1) |
| 0.6 ( 1.3) |
| 1.1 ( 2.2) |
|
| 1.0 ( 1.9) |
| 1.4 ( 2.3) |
| 1.5 ( 2.6) |
|
| 1.8 ( 3.8) |
| 2.9 ( 4.2) |
| 3.7 ( 7.6) |
|
| 2.3 ( 5.0) |
| 4.0 ( 5.8) |
| 5.6 (11.3) |
|
| 1.1 ( 2.1) |
| 1.3 ( 3.1) |
| 2.2 ( 4.5) |
|
| C |
| 5.4 (10.3) |
| 9.2 (13.0) |
| 12.2 (25.5) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.8 ( 4.5) |
| 4.7 ( 9.4) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 1.7 ( 2.6) |
| 2.6 ( 4.6) |
| 5.2 ( 9.9) |
|
| 1.2 ( 1.9) |
| 1.6 ( 3.3) |
| 3.8 ( 6.8) |
|
| 0.7 ( 1.1) |
| 0.6 ( 1.0) |
| 1.5 ( 2.8) |
|
| 0.9 ( 1.8) |
| 1.2 ( 2.1) |
| 1.3 ( 2.1) |
|
| 1.3 ( 2.6) |
| 2.0 ( 3.5) |
| 2.6 ( 5.0) |
|
| D50 |
| 4.2 ( 7.7) |
| 6.8 (10.2) |
| 7.7 (15.6) |
|
| 0.6 ( 1.1) |
| 0.6 ( 1.3) |
| 1.1 ( 2.2) |
|
| 1.6 ( 2.6) |
| 2.5 ( 4.5) |
| 5.2 ( 9.9) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 0.6 ( 1.3) |
| 1.0 ( 1.5) |
| 1.5 ( 3.1) |
|
| 1.5 ( 3.2) |
| 2.5 ( 3.7) |
| 4.0 ( 8.1) |
|
| 2.1 ( 4.4) |
| 3.6 ( 5.5) |
| 6.0 (11.9) |
|
| 1.3 ( 2.4) |
| 1.2 ( 2.6) |
| 2.9 ( 5.0) |
|
| D55 |
| 4.8 ( 9.0) |
| 7.8 (11.6) |
| 9.1 (18.7) |
|
| 1.0 ( 1.9) |
| 1.4 ( 2.3) |
| 1.5 ( 2.6) |
|
| 1.1 ( 1.8) |
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 3.8 ( 6.8) |
|
| 0.6 ( 1.3) |
| 1.0 ( 1.5) |
| 1.5 ( 3.1) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 0.9 ( 1.9) |
| 1.5 ( 2.4) |
| 2.5 ( 5.0) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.1) |
| 2.6 ( 4.2) |
| 4.5 ( 8.7) |
|
| 1.3 ( 2.0) |
| 1.1 ( 1.8) |
| 1.7 ( 2.8) |
|
| D65 |
| 5.6 (10.9) |
| 9.2 (13.6) |
| 11.4 (23.7) |
|
| 1.8 ( 3.7) |
| 2.8 ( 4.2) |
| 3.7 ( 7.6) |
|
| 0.7 ( 1.1) |
| 0.5 ( 0.9) |
| 1.5 ( 2.8) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.5 ( 3.6) |
| 4.0 ( 8.1) |
|
| 0.9 ( 1.9) |
| 1.5 ( 2.3) |
| 2.5 ( 5.0) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 0.6 ( 1.3) |
| 1.1 ( 1.8) |
| 2.0 ( 3.8) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.1 ( 3.6) |
| 1.9 ( 3.4) |
|
| D75 |
| 6.2 (12.1) |
| 10.2 (15.0) |
| 13.2 (27.4) |
|
| 2.4 ( 5.0) |
| 3.9 ( 5.6) |
| 5.6 (11.3) |
|
| 0.9 ( 1.8) |
| 1.2 ( 2.0) |
| 1.3 ( 2.1) |
|
| 2.2 ( 4.5) |
| 3.6 ( 5.3) |
| 6.0 (11.9) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.6 ( 4.1) |
| 4.5 ( 8.7) |
|
| 0.7 ( 1.3) |
| 1.1 ( 1.8) |
| 2.0 ( 3.8) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|
| 2.0 ( 4.4) |
| 3.1 ( 5.0) |
| 3.6 ( 6.9) |
|
| E |
| 4.4 ( 7.7) |
| 7.5 (10.5) |
| 9.8 (20.5) |
|
| 1.1 ( 2.1) |
| 1.3 ( 2.9) |
| 2.2 ( 4.5) |
|
| 1.3 ( 2.6) |
| 2.0 ( 3.6) |
| 2.6 ( 5.0) |
|
| 1.4 ( 2.4) |
| 1.2 ( 2.5) |
| 2.9 ( 5.0) |
|
| 1.3 ( 2.1) |
| 1.1 ( 1.8) |
| 1.7 ( 2.8) |
|
| 1.6 ( 3.2) |
| 2.1 ( 3.6) |
| 1.9 ( 3.4) |
|
| 2.0 ( 4.5) |
| 3.1 ( 4.9) |
| 3.6 ( 6.9) |
|
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
| 0.0 ( 0.0) |
|